var box = ‘你好’;
box = 100;
box最后结果是100的数字类型的并且是全局,可以自动转换(但是不推荐污染全局环境)
//还有关于var在function里面的细节
var a=123; //一个全局的a变量,不管哪里都能访问的到它
function run(){
alert(a) //当一个函数里面有变量时,它首先是在函数里面找有没有这个变量
//当有时,优先获取函数里面的变量,没有时就去全局环境中找
}
run(); //这里的结果是:123
------------------------------------
//函数有var情况下
function run(){
alert(a); //首先程序运行到了这里,就会检查在这整个函数中有没有a这个变量发现有var a,
说明声明了一个a变量,在这个函数里面是有a变量的,那就使用这个函数里面的a变量,但是
这一步是在var a之前写的说明了找到了a变量但是没有赋到值,所以这里是undefined
var a=1; //程序到这里,说明值已经赋给了a变量,a变量有值了。
alert(a); //优先使用函数里面的变量,所以是1
}
run();
等同于
function run(){
var a;
alert(a);
a=1; //这里修改的不是全局中的a变量而是函数中的a变量
alert(a);
}
run();
-----------------------------------
//函数没有var情况下
function run(){
alert(a); //程序到这里,检查整个函数有没有定义a变量发现没有var a,说明就是没有a变量,那就去全局中找,所以这里是123
a=1; //在没有var的情况下说明定义了全局变量a,并且是覆盖了之前定义好的a变量
alert(a); //函数里没有var a,就去全局中找,说明这里是1
}
run();
var nihao =’好’,
buhao = 100
可以这样声明变量
传递赋值:相互独立,互补干扰。
例如var a=3; var b=a; b=4; a仍然等于3。
引用赋值:修改我也是修改你。
在js,数组,对象,函数默认都是引用赋值
例如var a={age:44} ;var b=a ; b.age=45, a对象的age属性也变成了45。
——————————————
数据类型
typeof 检测返回类型,一般返回的结果是 《js数据类型检测》
undefined
boolean
string
number
object
function
isNaN()判断一个对象是否是数字 不是数字显示TRUE
例如isNaN(25)是一个数字 返回 false
注意:
isNaN(’12’) ’12’字符串数字,自动转化为数字
isNaN(‘true’) true自动转化为1
Number(‘070’) 字符串数字转数字类型 结果70
Number(‘08.90′) 返回8.9
Number(”) 返回0
第一个参数接受字符串,第二个参数接受要转化的多少进制(一般我们转化的是10进制推荐写上10进制)
parseInt()只能把字符串转成整数
parseInt(’23lee’,10) 返回23
parseInt(‘lee23lee’,10) 返回 NaN
parseInt(‘1dfdf23lee’,10) 返回 1
parseInt(‘12.12’,10) 返回 12
parseInt(”) 返回 NaN
parseFloat() //只能解析10进制,没有第二个参数
parseFloat(‘sdf123sdf’) //NaN 不是数字类型
parseFloat(‘123sdf’) //123
parseFloat(‘123.5sdf’) //123.5
parseFloat(‘123.5.5sdf’) //123.5
parseFloat(‘00123.5.5sdf’) //123.5
字符串在JS 中单引号和双引号一样效果
转化字符串类型
box.toString() //默认转化10进制
toString() 不能转化 NULL 和 undefined
String(box) 可以强制转化 NULL 和 undefined
var num=10;
num.toString(2)
num.toString(8)
num.toString(10)
num.toString(16)
对象
两个不同类型的数字计算可以得出正确的结果
JS会把数字自动转化为数字类型
var box = new Object();
new Number(50)
new String(‘lee’)
获取对象里面属性个数
//不支持IE8,支持IE9以上 Object.getOwnPropertyNames(a).length
运算符
转化为数字类型
box++
++box
结果都是自身加1,区别在于赋值。


数字加字符串 结果是字符串类型
跟NaN计算的结果类型都是NaN
比较符
‘3’>22 如果字符串是个数,JS自动转换数字类型
‘3’>’22’如果字符串是十位数JS只去第一位比较3>2
‘a’>’b’ 97>98 比较
在JS逻辑运算中:
如果使用 && ,只要第一位是false就取第一位的结果没必要
运行第二位。如果第一位是true,就要去运行第二位的结果,直接
就取第二位结果的值。
*因为&&必须同时满足两个条件,第一个条件假,直接取第一个结果
没必要去看第二位了,如果第一个位是真,还要去判断第二位。
如果使用 || 的时候,只要第一条true,就没必要去判断第二位了,
因为|| 只要满足一个条件就行
!可以用于任何数据类型,结果都是先取布尔值在取反。
—————————————————–
流程控制 语句
for–in语句是遍历处理对象的属性名,和数组的索引用的
var box= {‘name’:’你好’,’age’:12}
for(var x in box){
alert(x)
}
break 立刻推出循环,后面的循环不进行。 只能用在循环 和switch
with作用于对象
with(box){
var n = name; 可以省略掉.box就可以打印出name的值
alert(n);
}
switch
var type=row.file_name.split('.')[1];
switch (true)
{
case type=='rar':
return "<img style=\"height: 80px;width: auto\" src=\""+window.location.protocol+"//"+window.location.host+"/images/rar.png \"/>";
break;
case type=='docx':
return "<img style=\"height: 80px;width: auto\" src=\""+window.location.protocol+"//"+window.location.host+"/images/docx.png \"/>";
break;
case type=='jpg' || type=='gif' || type=='png' || type=='bmp':
return "<img style=\"height: 80px;width: auto\" src=\""+window.location.protocol+"//"+window.location.host+"/images/"+row.file_name+"\"/>";
break;
default:
return "<img style=\"height: 80px;width: auto\" src=\""+window.location.protocol+"//"+window.location.host+"/images/other.png \"/>";
break;
}
var arr=[a,b,c]
for–of
for(var x of arr){
alert(x) //直接遍历出结果而不是索引
}
forEach //兼容IE9以上,遍历数组里面内容
array.forEach(function(value, index, array) { //值,索引,遍历数组本身
//代码alert(value, index, array)
});
—————————-
函数
function box(参数1,参数2){ 函数声明
}
box(参数1,参数2) 函数调用
函数声明可以放在 函数调用 上下任意位置
return返回值
函数声明 里面有return返回值的时候,
调用函数 调用 函数声明里面的返回值,在把值返回给调用函数
function box(){
alert(‘你好’);
}
box(); 直接就调用,并执行了 box()函数声明。
function box(){
reture’你好’;
}
box(); 调用执行了box()函数声明,里面有reture的话就
把值返回给调用函数box(),相当于var box =’你好’;
函数声明里面遇到第一个reture后面的代码不在执行
function box(){
reture’你好’; //从这里开始后面的都不被执行
alert(‘不好’);
}
arguments[i] //有点类似数组或者对象作用
使用argument是当box()里面的参数不确定使用多少个的情况下使用的。
例如
function box(){
reture arguments[0],arguments[1],arguments[2]
}
box(‘你’,29,’不好’)
分别一一对应
如果出现相同的 几个函数声明 就只能执行最后一函数声明

————————————————-”
数组 对象
var box={
‘name’:’你好’;
};
var box={
name:’你好’;
};
加不加引号都行。
输出方式:
box.name
box[‘name’]
对象中的方法就是函数,就是属性的值是函数。
var box={
name:’你好’;
run:nihao(); //方法
};
function nihao(){
return 123;
}
调用时box.run()
delete box.run()
函数中的参数可以存放对象
function nihao(obj){
}
var obj ={}
对象中的方法
栈方法
对数组操作的函数
| .push(‘123’) //在数组末尾添加,返回添加后数组的长度 | 1 |
| .pop() //删除数组末尾最后一位,返回被删除的那项内容 | 1 |
| .shift() //删除数组最前一位,返回被删除的那项内容 | 1 |
| .unshift(‘123′,’456’) //在数组最前面添加内容,返回添加后数组的长度(IE8之前版本返回有问题) | 1 |
| .sort() //升序 | 1 |
| .reverse() //降序 | 1 |
| .concat(‘123’,[‘456′,’789’]) //追加数组 | 1 |
| .slice() //筛选 (不会影响原来数组)索引从0开始 | 1 |
| .splice() //删除,插入,替换 索引从0开始,(影响原有数组) | 1 |
| ‘hello world’.indexOf(‘wo’) //6 查找指定内容所在索引的位置,索引从0开始 | 1 |
| .lastIndexOf() //删除,插入,替换 索引从0开始 | 1 |
| .join() //获取数组里所有元素,并拼接成一行字符串 | 1 |
.push()为数组末尾添加内容
例如
alert(box.push(‘计算机’,’江苏’)) //弹出的是添加内容后的数字长度
alert(box.pop()) //弹出移除的最后一条的内容
同上
shift() //删除开头的元素
unshift() //开头添加元素
注意在IE浏览器中unshift()可以在开头添加元素,但是无法。
array.prototype.map
例子:
var arr=[10,5,30];
var newarry=arr.map(function(value,index,array){ //值,索引,整个数组
alert(array)
});
不会改变原来数组,而是创建一个新数组
检测是否为数组 isArray
Array.isArray(value) //检测value值是否为数组。返回布尔值,只兼容IE9以上
检测数组里是否存在该值 includes
arr.includes(‘cat’) //返回布尔值
数组去重
const arr = [3, 5, 2, 2, 5, 5]; const unique = [...new Set(arr)]; // [3,5,2]
或者
Array.from(new Set([1, 1, 2, 3])); // [1, 2, 3]
字符去重
let str = [...new Set("ababbc")].join("");
console.log(str);
// 'abc'
并集、交集、差集
let a = new Set([1, 2, 3]);
let b = new Set([4, 3, 2]);
// 并集
let union = new Set([...a, ...b]);
// Set {1, 2, 3, 4}
// 交集
let intersect = new Set([...a].filter(x => b.has(x)));
// set {2, 3}
// 差集 (以a为准,去掉与b一样的元素)
let difference = new Set([...a].filter(x => !b.has(x)));
// Set {1}
——————————————————
JS排序
var box=[1,2,3,4,5]
逆向排序:
alert(box.reverse()) //弹出54321
sort() 从小到大排序

var arr = [1, 4, 5, 2, 3, 9, 0, 7, 6];
var temp;
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (var j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[i] > arr[j]) {
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
}
console.log(arr); //小到大排序
var box=[1,2,3,4,5,10]
box.sort(compare);
concat()追加数组
var box=[‘你好’,’他好’]
var box2=box.concat(‘计算机’);
alert(box2) //弹出 你好,他好,计算机
slice()筛选数组
var box=[‘你好’,’他好’,’海口’,’海南’]
var box2=box.slice(1); //索引是0,从第1个元素开始包括1选取到后面的元素
box2 //内容是 ‘他好’,’海口’,’海南’
var box2=box.slice(1,3); //索引是0,从第1个元素开始包括1选取到后面的第3个元素
不包括3
box2 //’他好’,’海口’
splice() //返回的是删除的内容并且是一个数组,如果没有内容删除返回一个空数组
splice()删除功能
var box=[‘你好’,’他好’,’海口’,’海南’]
var box2=box.splice(0,2); //从第0个元素选2个删除,返回一个数组 ‘你好’,’他好’
alert(box) //’海口’,’海南’
splice()插入功能
var box=[‘你好’,’他好’,’海口’,’海南’]
box.splice(1,0,’海岛’) //在索引1的位置开始前面插入
alert(box) // ‘你好’,’海岛’,’他好’,’海口’,’海南’
splice()替换功能
box.splice(1,1,’海岛’) //在索引1的位置开始选1项替换成’海岛’
alert(box) // ‘你好’,’海岛’,’海口’,’海南’
indexOf()
————————————————————————-
Function类型再次深入讲解
声明一个函数
function box(){代码}
var box = function() {}
function也属于对象类型
在函数中,如果里面的参数也函数函数,那么参数里面的
函数可以做为数值传入,也可以作为一个函数传入。(就是函数里有函数)
函数使用递归,自调用的时候最好使用callss属性,图
函数是box

如果函数box改名了之后函数内部的box也会改名字,为了方便
使用arguments.callss(),就是函数内部自己。
全局中的this也是默认调用了window
var color=’红色’;全局变量其实就是window的一个属性
alert(window.color) //弹出红色的
要想知道函数里面传多少参数使用length
function box(…){}
box.length
apply用法如图

this是全局,因为box的作用范围是全局
如果参数多的话就使用arguments

call()方法
call()方法和apply()只是传递的参数方式不一样而已
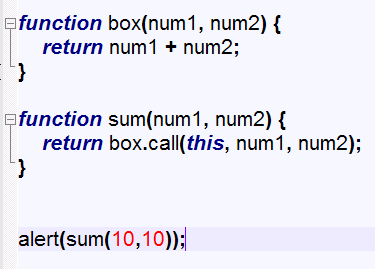
call()方法和apply()其实功能是改变作用域
例如让某一个函数中的this冒充全局中的某一个值,或者局部中的某一个值

语意是:我要去模仿别人.call( 被我模仿的人 )
我是function类型,
被我模仿的人 是object类型
—————————————————————
内置对象
就是js本身就有的
GLobal// window一般代替GLobal
Math
手工将中文编码为URL字符为了能够浏览器识别
只编码中文
var box=”//Lee李”;
encodeURI(box) //只将李编码
encodeURIComponent(box)//全部编码
如果要显示给用户看必须解码,对应的解码是
decodeURI()
decodeURIcomponent()
encodeURI 和 decodeURI
encodeURI不编码字符有82个:!,#,$,&,’,(,),*,+,,,-,.,/,:,;,=,?,@,_,~,0-9,a-z,A-Z
可以理解只针对中文编码
encodeURI('http://localhost:8080/pro?a=1&b=张三&c=aaa')
结果:http://localhost:8080/pro?a=1&b=%E5%BC%A0%E4%B8%89&c=aaa
decodeURI //解码
encodeURIComponent 和 decodeURIComponent
对所有的特殊和中文都编译
encodeURIComponent('http://localhost:8080/pro?a=1&b=张三&c=aaa')
结果:http%3A%2F%2Flocalhost%3A8080%2Fpro%3Fa%3D1%26b%3D%E5%BC%A0%E4%B8%89%26c%3Daaa
decodeURIComponent //解码
escape 和 unescape
escape不编码字符有69个:*,+,-,.,/,@,_,0-9,a-z,A-Z。
escape('http://localhost:8080/pro?a=1&b=张三&c=aaa')
结果:http%3A//localhost%3A8080/pro%3Fa%3D1%26b%3D%u5F20%u4E09%26c%3Daaa
unescape //解码
eval();将字符窜里的js代码解析并执行
‘alert(‘你好’)’ //不被执行
eval(‘alert(‘你好’)’) //执行
Math.min(3,6,9) //求最小值
Math.min(3,6,9) //求最大值
Math.ceil(25.1) //得到26
Math.floor(25.9) //得到25
Math.round() //四舍五入
Math.random() //默认取0~1之间的数字
Math.random()*9+5 //取5~14之间的数 (最大值是 10+5 )
———————————————————–
js面向对象
创建对象
var box =new Object();
box.name=’lee’;
box.age=100;
box.run=function(){ //方法
return this.name+this.age; //这里的this是box函数自己。
}
工厂模式
如果很多函数的属性名相同就使用工厂模式
function createObject(name,age){
var obj =new Object();
obj.name=name;
obj.age=age;
obj.run=function(){
return this.name+this.age;
};
return obj; //必须返回不然得不到一个对象
};
var box1=createObject(‘lee’,100);
var box2=createObject(‘lee’,100);
alert(box1.run());
alert(box2.run());
工厂模式缺点就是创建调用出来的函数不知道是哪个一个工厂模式的函数。
解决方法是使用,构造函数(构造函数其实就是改良后的工厂模式)
function Desk(name,age){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
this.run=function(){
return this.name+this.age;
}
}
var box1=new Desk(‘kkk’,500);
alert(box1 instanceof Desk); //检测box1实例对象的类(或者构造函数)是否为Desk,如果是返回true
1,构造函数后台已经自动创建var obj =new Object
2,也自动返回了return Desk函数。
构造函数使用注意:
1,创建构造函数首字母大写
2,调用函数new 首字母也要大写
冒充函数call
var 0 =new Object();
Desk.call(o,’lee’,100); //o冒充成了构造函数Desk,o就具备Desk功能
alert(o.run());
function Desk(name,age){ //构造函数
this.name=name;
this.age=age; //实例属性
this.run=function(){ //实例方法
return this.name+this.age;
}
}
<—————————————>
function Box(){} //构造函数里面什么都没有,如果有就是实例属性和实例方法
Box.prototype.name=’lee’; //原型属性
Box.prototype.age=100; //原型属性
Box.prototype.run=function(){ //原型方法
return this.name+this.age+’运行中..’;
}
实例 和 原型唯一区别就是实例不共享代码,原型共享
原型代码都加了一个prototype才能引用到原型代码
构造函数图解:
原型图解:
一个对象是用实例还是原型使用
alert(Box.prototype.isPrototypeOf(box));
如果实例 和 原型同时有属性name或者是相同的属性名,都
先查找实例里面的属性在找原型的属性
优先级顺序是
box1.name=’jack’;> this.name=’chen’;>Box.prototype.name=’lee’;
删除实例属性
delete box1.name; //删除实例,这样直接就是访问原型属性name的值
删除原型属性
delete Box.prototype.name;
覆盖原型属性
Box.prototype.name=’kkk’;
检查实例中某属性是否存在
alert(box.hasOwnProperty(‘name’));
检查原型中某属性是否存在
function ys(object,property){
return !object.hasOwnProperty(property)&&(property in object)
}
调用函数 ys(box1,’name’);
检查实例和原型中某属性是否存在
alert(‘name’ in box1);
原型字面量写发(字面量是将代码封装感觉)
function Box(){}
Box.prototype={
constructor:Box, //强制指向Box
name:’lee’;
age:100,
run:function(){
return this.name+this.age+’运行中…’;
}
}
Box.prototype={ //重写原型之前的属性就没有了
age:100,
}
var box = new Box();
alert(box.constructor);
JS中许多内置方法都使用了原型对象。
JS内置方法是否使用了原型使用
alert(Array.prototype.sort);
扩展JS内置方法
1,首先判断方法名字是否有重复
2,代码
String.prototype.addstring=function(){
return this+’,被添加!’;
}
var box =’lee’;
alert(box.addstring());
原型需要共享的地方才共享,需要独立的地方才独立
(数组,函数,对象默认是引用赋值)
例如:
function Box(){} //实例
Box.prototype={ //原型
constructor:Box,
name:’lee’,
age:100,
family:[‘哥哥’,’姐姐’,’妹妹’],
run:function(){
return this.name+this.age+’运行中’;
}
}
var box1 =new Box();
box1.family.push(‘弟弟’); //这里在数组添加了’妹妹’
var box2 =new Box();
alert(box2.family); //弹出的数组有弟弟,这里实现了共享
为了保证该独立的地方需要独立,该共享的地方共享,只需要将
数组,函数,对象存放在实例代码中,即可。
继承
function Box(){ //爷爷
this.name=’lee’;
}
function Desk(){ //儿子
this.age=100;
}
function Table(){ //孙子
this.le=’aaaa’;
}
继承方法
Desk.prototype=new Box(); //儿子用原型继承了爷爷
Table.prototype=new Desk(); //孙子又继承了儿子
现在孙子的原型继承了儿子,爷爷构造函数和原型。
对象冒充
function Box(age){
this.name=[‘lee’,100];
this.age=age;
}
Box.prototype.run=function(){
return this.name+this.age+’运行中’;
}
function Desk(age){ //Desk构造函数冒充Box构造函数,对象冒充可以传参数
Box.call(this,age)
}
在对象冒充中冒充构造函数只能使用构造函数的代码,而不能使用原型代码
这里需要冒充原型代码
Desk.prototype=new Box(); //这里就可以使用Box.prototype.run里面的代码了实现了共享原型代码
BOM常用属性和方法

window.alert();
confirm(‘你好’)//有确定,取消按钮;确定是1,取消是0
例如:
if(confirm(‘请选择’)){
alert(‘你点了确定’);
}else{
alert(‘你点了取消’);
}
open(‘http://www.baidu.com’);//弹出新页面并打开百度
open(‘http://www.baidu.com’,’_parent’);//本窗口加载
window.open(“http://google.com/”,’新开googleWin1′,”height=300, width=300, top=0, left=0,toolbar=no, menubar=no, scrollbars=no, resizable=no, location=n o, status=no”)
opener//子窗口操作父窗口
例如在子窗口上写
document.onclick=function(){
opener.document.write(‘子窗口让我输出子’);
}
var width=window.innerWidth;
var heigh=window.innerHeight;
if(typeof width !=’number’){
if(document.compatMode==’CSS1Compat’){
width=document.documentElement.clienWidth;
height=document.documentElement.clientHeight;
}else{
width=document.body.clientWidth;
height=document.body.clienHeight;
}
}
var time=setTimeout(function(){ //2秒后执行代码
代码;
},2000);
clearTimeout(time); //取消超时操作
var box=setInterval(function(){ //两秒执行一次代码
代码;
},2000);
clearInterval(box);
localtion.hash //#21
localtion.port //:8080
localtion.search //?id=2
<!--http://localhost/mytest/qqvip.html#123--> window.location.hash ; // #123 <!--http://localhost:8080/mytest/qqvip.html--> window.location.host ; // localhost:8080 <!--http://localhost:8080/mytest/qqvip.html--> window.location.hostname ; // localhost <!--http://localhost/mytest/qqvip.html?di=123#123--> window.location.href ; //http://localhost/mytest/qqvip.html?di=123#123 <!--http://localhost/mytest/qqvip.html?di=123#123--> window.location.pathname ; ///mytest/qqvip.html window.location.port ; //8080 window.location.protocol ; //http: window.location.search; //?di=123
substring(4) //删除字符串前4个字符;
// 获取url以?为准后面的参数 http://www.vc.com/v2/crowdfunding?category=all&aa=bb
function GetRequest() {
var url = location.search; //获取url中"?"符后的字串
var theRequest = new Object();
if (url.indexOf("?") != -1) {
var str = url.substr(1);
strs = str.split("&");
for(var i = 0; i < strs.length; i ++) {
theRequest[strs[i].split("=")[0]]=unescape(strs[i].split("=")[1]);
}
}
return theRequest;
}
console.log(GetRequest()); //{category: "all", aa: "bb"}
split(‘&’) //将字符串带有&符号的用逗号代替,并且封装为数组。
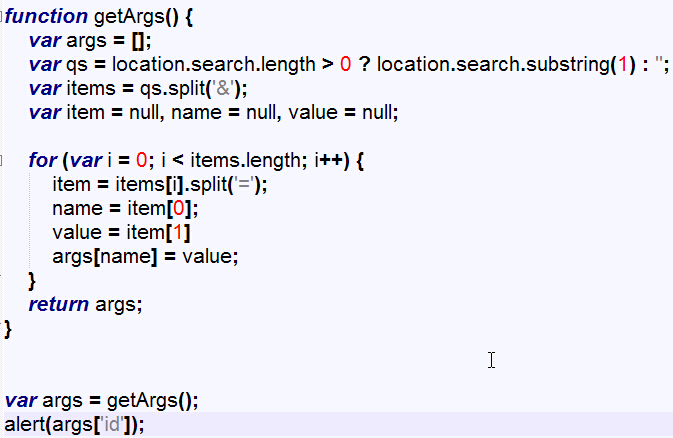
location.assign(‘http://baidu.com’); //URL跳转,浏览器能点击返回上页功能。
location.replace(‘http://www.baidu.com’); //同样是跳转,但是此效果跳转就不能使用浏览器自
带的后退功能了。
history (主要功能是浏览器的后退前进)
history.length //查询几条历史记录
history.back(); //上一条记录 等效 history.go(-1);
history.forward(); //下一条记录 等效 history.go(1);
history.go(-2); //直接前进返回历史记录前面2页
history.go(2); //直接下2页
—————————————————————–
时间Date()
时间戳就是一串很长的数字如:1462514341409,其实这是毫秒数,如果要换成秒就除以1000即可。
这一串毫秒数其实就是1970年01月01日00时00分00秒到现在我们此刻的时间。
如果我们想知道1970年01月01日00时00分00秒到此刻我们过了多少秒:new Date().getTime()/1000即可
document.title= (new Date( (Date.UTC(2007,5,7,11,22,23))-(Date.UTC(2007,5,6,11,22,23)))).toTimeString(); document.title=new Date(); // Fri May 06 2016 13:46:47 GMT+0800 document.title=+new Date(); // 1462514341409 document.title=new Date(2007,5,6,11,40,50,15);// Wed Jun 06 2007 11:40:50 GMT+0800 (注意月的索引是0开始0代表一月) document.title=new Date(1462514341409); // Fri May 06 2016 13:59:01 GMT+0800
//本地格式化(用处不大没一个方法是所有浏览器显示一致的)
document.title=new Date().toDateString(); //Fri May 06 2016
document.title=new Date().toTimeString(); //14:38:54 GMT+0800
document.title=new Date().toLocaleDateString(); //2016/5/6 IE显示 2016年5月6日
document.title=new Date().toLocaleTimeString(); // 下午2:41:49 IE显示 2:41:49
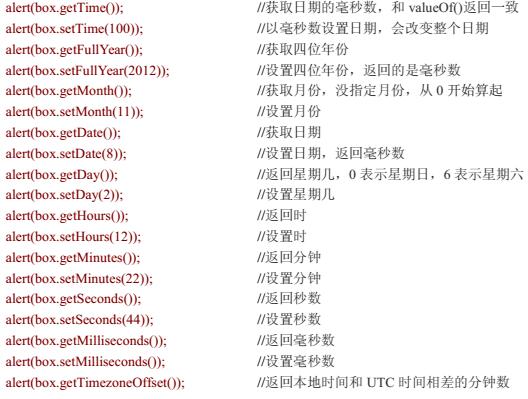
//时间组件
document.title=new Date().getTime(); // 1462514341409 当天时间戳 时间格式 类似:2018-10-31 23:59:59
document.title=new Date().getFullYear(); // 获取年份2016
document.title=new Date().getMonth()+1; // 获取月份 (注意月份索引是0开始0代表一月)
document.title=new Date().getDate(); //获取日
document.title=new Date().getHours(); //时
document.title=new Date().getMinutes();//分
document.title=new Date().getSeconds();//秒
new Date().getDay() //获取当天星期几,返回0-6,0对应星期天,1-6对应星期一到星期六
new Date('2009/10/28').getDay() //具体时间星期几
new Date(2004, 2, 0).getDate() //2004年2月份一共几天
Date.parse(new Date("2018-10-31 23:59:59")) // 2018-10-31 23:59:59 转为 时间戳 IE只识别2018/10/31
Date.parse('2019-10-26T17:45:27.074') // 带T时间格式2019-10-26T17:45:27.074 转 1572083127074,移步看
也可以修改把get改成set就行 还支持UTC函数跟不用UTC函数的主要区别在于获取小时不同,例如: getUTCHours() //获取小时,记得要减去8个小时才是北京时间 new Date().getUTCHours()-8 //北京时间,24小时制
<script type="text/javascript">
function GetDateStr(AddDayCount) {
var dd = new Date();
dd.setDate(dd.getDate()+AddDayCount);//获取AddDayCount天后的日期
var y = dd.getFullYear();
var m = dd.getMonth()+1;//获取当前月份的日期
var d = dd.getDate();
return y+"-"+m+"-"+d;
}
document.write("前天:"+GetDateStr(-2));
document.write("<br />昨天:"+GetDateStr(-1));
document.write("<br />今天:"+GetDateStr(0));
document.write("<br />明天:"+GetDateStr(1));
document.write("<br />后天:"+GetDateStr(2));
document.write("<br />大后天:"+GetDateStr(3));
</script>
http://www.nowamagic.net/librarys/veda/detail/1655
//0000-00-00T00:00:00.074 转 时间戳
+new Date('2019-10-26T17:45:27.074')
//时间戳 转 2019-05-29 11:35:19
function formatDateTime(inputTime) {
var date = new Date(inputTime);
var y = date.getFullYear();
var m = date.getMonth() + 1;
m = m < 10 ? ('0' + m) : m;
var d = date.getDate();
d = d < 10 ? ('0' + d) : d;
var h = date.getHours();
h = h < 10 ? ('0' + h) : h;
var minute = date.getMinutes();
var second = date.getSeconds();
minute = minute < 10 ? ('0' + minute) : minute;
second = second < 10 ? ('0' + second) : second;
return y + '-' + m + '-' + d + ' ' + h + ':' + minute + ':' + second;
}
//时间段判断
var now_time=new Date().getFullYear()+'-'+(new Date().getMonth()+1)+'-'+new Date().getDate();
var curr_time= new Date().getTime(); // Date.parse(new Date(now_time+" 18:30:00")); //new Date().getTime();
// 白天黑夜变化
function dayState() {
//黑
// 00:00 到 6:30
// 18:30 到 23:59
//白
// 06:30 到 12:00
// 12:00 到 18:30
//注意苹果系统要装-转/ *(/macintosh|mac os x/i.test(navigator.userAgent))?"2020/4/3 23:59:59":"2020-4-3 23:59:59"
var new_now_time = (/macintosh|mac os x/i.test(navigator.userAgent))? now_time.replace(/\//ig,'-') :now_time;
if( //黑夜
(Date.parse(new Date(new_now_time+" 05:00:00"))<= curr_time && curr_time <Date.parse(new Date(new_now_time+" 06:00:00"))) ||
(Date.parse(new Date(new_now_time+" 19:00:00"))<= curr_time && curr_time <Date.parse(new Date(new_now_time+" 20:00:00")))
){
console.log('黑');
}else{
console.log('白');
}
}
dayState();
2019-05-10 14:40:18 时间加1天
var dateTime = new Date(this.endTime) dateTime = dateTime.setDate(dateTime.getDate()+1) dateTime = new Date(dateTime).toLocaleDateString()
判断是否过凌晨
<script src="js/jquery.cookie.js"></script>
var new_day=GetDateStr(0);
function GetDateStr(AddDayCount) {
var dd = new Date();
dd.setDate(dd.getDate()+AddDayCount);//获取AddDayCount天后的日期
var y = dd.getFullYear();
var m = dd.getMonth()+1;//获取当前月份的日期
var d = dd.getDate();
return y+"-"+m+"-"+d;
}
setInterval(function () {
if( !(window.localStorage.new_day || $.cookie('new_day')) ){ //都没值也就是第一次访问的时候去执行
console.log('第一次');
window.localStorage.new_day=new_day;
$.cookie('new_day', new_day);
}else{
var newDate=new Date();
var year_mon_d=newDate.getFullYear()+'-'+(newDate.getMonth()+1)+'-'+newDate.getDate();
if( year_mon_d !=window.localStorage.new_day || year_mon_d !=$.cookie('new_day') ){
console.log('过了凌晨了');
window.localStorage.new_day=GetDateStr(0);
$.cookie('new_day', GetDateStr(0));
}else {
console.log('还没过一天');
}
}
},500);
//判断当前时间是否在指定时间段内
function nowInDateBetwen (d1,d2) {
//如果时间格式是正确的,那下面这一步转化时间格式就可以不用了
// var dateBegin = new Date(d1.replace(/-/g, "/"));//将-转化为/,使用new Date
// var dateEnd = new Date(d2.replace(/-/g, "/"));//将-转化为/,使用new Date
var dateBegin = new Date(d1);//将-转化为/,使用new Date
var dateEnd = new Date(d2);//将-转化为/,使用new Date
var dateNow = new Date();//获取当前时间
var beginDiff = dateNow.getTime() - dateBegin.getTime();//时间差的毫秒数
var beginDayDiff = Math.floor(beginDiff / (24 * 3600 * 1000));//计算出相差天数
var endDiff = dateEnd.getTime() - dateNow.getTime();//时间差的毫秒数
var endDayDiff = Math.floor(endDiff / (24 * 3600 * 1000));//计算出相差天数
if (endDayDiff < 0) {//已过期
return '已结束';
// return false
}
if (beginDayDiff < 0) {//没到开始时间
return '报名中';
// return false;
}
return '授课中';
// return true;
}
console.log(nowInDateBetwen('2022-7-12 11:11:11','2022-7-12 11:11:12'))
DOM
<ul><li></li> </ul>
document.getElementsByTagName('li')[0] //返回的是数组
<input type="text" name="test">
document.getElementsByName('test')[0] //寻找有name="test" 的元素
box.getAttribute('aaa') //获取元素属性包括自定义属性,例如aaa="bbb"但获取class属性IE不兼容
box.setAttribute('title','设值')
box.removeAttribute('style')
box.attributes[0].nodeName //获取此元素的第一个属性的属性名称
box.attributes[0].nodeType
box.attributes[0].nodeValue
box.className //获取元素class属性值 box.Id box.title box.nodeName //元素名称 box.nodeType // 1为元素 2为属性 3为文本 box.nodeValue //利用childNodes获取到文本节点时才能使用nodeValue获取纯文本内容和设置它的值
<div> 我<em>你</em>他 </div> box.childNodes.item(0).nodeValue //我 box.firstChild.nodeValue //同上 box.lastChild.nodeValue //获取最后一个文本节点 box.parentNode //获取此元素的父元素 box.lastChild.previousSibling //此文本节点的上一个同级的元素或文本节点 box.firstChild.nextSibling //此文本节点 的下一个同级的元素或文本节点
创建节点
var div=document.createElement(‘div’); //创建一个空的div元素
document.getElementsByTagName(‘body’)[0].appendChild(div); //在body元素的内部最后面插入div
此节点的父节点.insertBefore(插入新的标签,在此节点的前面插入新的标签)
box.parentNode.insertBefore(div,box)// 就可以在box元素的前面插入一个div标签
被替换元素.parentNode.replaceChild(新元素,被替换元素); //元素替换
获取被克隆的元素或者文本节点.cloneNode(true); //true克隆标签和里面内容 ;false仅仅克隆标签
box.removeChild( box.firstChild ); //删除box里的第一个节点
宽、高
document.title=document.querySelector('div').clientWidth; //获取宽度 width+padding (如果有滚动条,宽度为width+padding-滚动条宽度)
document.title=document.querySelector('div').offsetWidth; //获取宽度 width+padding+border (如果有滚动调忽略不管)
document.title=document.querySelector('div').style.marginTop;
document.title=document.querySelector('div').style.paddingTop;
document.title=document.documentElement.clientWidth; //获取浏览器窗口宽度 (如果有滚动条要减去滚动条宽度)
获取class类名
HTML5提供一个
document.querySelector('.my') //仅仅是获取第一个class为my的DOM元素
document.querySelectorAll('.my') //获取全部class为my的DOM元素
如果为了兼容
只能使用document.getElementsByTagName('div')在用for一个个去判断了,效率极低
*清除空白节点
function cleanWhitespace(element)
{
for(var i=0; i<element.childNodes.length; i++){
var node = element.childNodes[i];
if(node.nodeType == 3 && /\s/.test(node.nodeValue)){
node.parentNode.removeChild(node);
}
}
return element;
}
关于DOM和BOM参考:《JavaScript 操作 DOM 的那些坑》
———————————————————-
递归
function digui(num){
if(num<=1){
return 1;
}else{
return num * arguments.callee(num-1);
}
}
console.log( digui(9) );
9x8x7x6x5x4x3x2x1
arguments.callee //arguments.callee 在哪一个函数中运行,它就代表哪个函数。
(function(){
var wo='fff';
console.log(arguments.callee); //打印出来的是此匿名函数
})();
/*—————————————————————————
es6 笔记
—————————————————————————*/
箭头
$('button').click(function () {
console.log(this); // <button></button>
window.setTimeout(function () {
console.log(this); //window
},1000)
});
不使用箭头函数this指向有问题乱跑,如果想让它依然指向$(‘button’)那就这么写:
$('button').click(function () {
console.log(this); // <button></button>
window.setTimeout(() =>{
console.log(this); // <button></button>
},1000)
});
比较
Object.is({},{})
其他比较没问题,主要注意一下比较:
NaN === NaN // false
Object.is(NaN, NaN) // true
0 === -0 // true
Object.is(0, -0) // false
-0 === +0 // true
Object.is(-0, +0) // false
对象合并
Object.assign(target, source1, source2)合并对象;(浅拷贝)
模板
以前变量要插入到字符串中都需要+来合并,例如:
var name="小陈" '我是'+name;
如果是少量的字符串和变量的话没什么问题,但是遇到比较多的字符串和变量拼接时,就容易混乱了。
现在e6的新方法是:
var name="小陈"
`我是${name}`
默认值
//以前为函数添加默认值的方法
function bb(a,b) {
var a=a||1;
var b=b||1;
document.title=a+b;
}
bb(2,2);
现在为函数添加默认值方法:
function bb(a=1,b=1) {
document.title=a+b;
}
bb(2,2);
Promise对象
reject函数的参数通常是Error对象的实例,表示抛出的错误;reject( new Error(‘错了’) );
//参数能接受数字、字符串或者一个new Error对象
resolve函数的参数除了正常的值以外,还可能是另一个Promise实例,表示异步操作的结果有可能是一个值,也有可能是另一个异步操作
//参数能接受数字、字符串或者是Promise对象返回状态
console.log(1)
var p1 = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
console.log(2)
setTimeout(function(){reject('失败');},3000)
});
var p2 = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
console.log(3)
resolve(p1); //p2接受的是p1的返回结果,p1是Promise,所以必须是resolve函数来接受
});
p2.then(function(value){ //p2会一直等待p1的返回结果才能执行回调,p2的回调基本就是相当于p1的回调了
console.log(value+'<------'); //p2成功回调
},function(error){
console.log(error+'<---3---'); //p2失败回调
});
console.log(4)
执行顺序:
1
2
3
4
失败<---3---
then
promise.then //promise的回调不仅等待promise返回的状态,还要等待其他JS业务逻辑完成后才执行,总是最后面执行 console.log(1) var promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) { console.log(2) var toggle=false; if (toggle){ resolve('成功'); //成功状态,并传参数 } else { reject('失败'); //失败状态,并传参数 } }); promise.then(function(value) { console.log(3) console.log(value+'<-------'); }, function(error) { console.log(3) console.log(error+'<-------'); }); console.log(4) 执行顺序: 1 2 4 3 失败<-------
console.log(1)
var promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
//这里面的代码会按正常顺序执行
console.log(2)
setTimeout(function(){
var toggle=false;
if (toggle){
resolve('成功');
console.log(3)
} else {
reject('失败');
console.log(4)
}
},4000)
});
promise.then(function(value) { //必须要等返回结果状态才能执行
console.log(5)
console.log(value+'<-------');
}, function(error) {
console.log(6)
console.log(error+'<-------');
});
console.log(7)
执行顺序:
1
2
7
4
6
失败<-------
catch
//推荐使用以下方法来处理错误
promise
.then(function(value){
//成功回调
})
.catch(function(error){
//promise失败状态 或者 then出错时候,就执行catch回调
});
等同于
promise
.then(function(value){
//成功回调
})
.then(null,function(error) {
//promise失败状态 或者 then出错时候,就执行catch回调
});
---------------------------------------------------
Promise 抛错时
例子:
var p1 = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
throw new Error('test'); //抛出错误
});
p1.then(function(){
//成功时回调
})
.catch(function(error){
console.log(error); //抛错回调被执行
})
---------------------------------------------------
then 抛错时
var p1 = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
resolve('成功');
});
p1.then(function(){
throw new Error('test'); //抛出错误
})
.catch(function(error){
console.log(error);
})
all
等待全部结果执行出来后才回调
var p1 = new Promise(function(resolve, reject){resolve('p1');});
var p2 = new Promise(function(resolve, reject){ setTimeout(function(){resolve('p2');},3000) });
var p3 = new Promise(function(resolve, reject){resolve('p3');});
//所有结果都是成功Promise.all才有成功回调,只要有一个就触发错误回调
Promise.all([p1,p2,p3]).then(function(value){ //回调触发要等待所有的p1,p2,p3执行完了才执行
console.log(value); //[ 'p1', 'p2', 'p3' ] 要等待3秒后才回调出数据
}).catch(function(){
console.log('出错')
});
-----------------------
Promise.all[fn1,fn2,fn3].then(function(){ //参数也可以传入函数,回调不管fn是否有延迟加载都会马上触发
});
/*—————————————————————————
class类
—————————————————————————*/
创建构造函数
class Run {
constructor(x, y) {
//构造函数
this.name=x;
}
}
等价
function Run(){
//构造函数
this.name=x;
}
为原型函数添加属性和方法
class Run {
constructor(x, y) {
//构造函数
this.name=x;
}
sayhello(){
//原型方法
}
}
或者
Object.assign(Run.prototype, {
sayhello:function (){
return 'hello';
}
});
等价
function Run(){
//构造函数
this.name=x;
}
Run.prototype.sayhello=function(){
//原型方法
}
声明私用变量和方法
class Wo{
constructor(){ //相当于构造函数
var myname='名字'; //私有变量,
var myfun=function () { //私有方法
return '私有方法'
}
this.getmyname=function () {
return myname+'<-----获取私有变量';
}
this.getmyfun=function () {
return myfun()+'<-----获取私有方法';
}
}
//constructor以外的都是原型方法和属性
string(){
console.log(this.getmyname())
console.log(this.getmyfun())
}
}
调用:(new Wo()).string()
继承
在es5中的继承用prototype,在es6中可以使用extends关键词
class Point {
constructor(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
class ColorPoint extends Point {
constructor(x, y, color) {
console.log(this); //用继承的方式创建的class类是没有this的,也就是ColorPoint没有this
super() //所以要使用super(),这样ColorPoint才能用属于自己的this
this.xx='haha1' //引入this后才能像这样定义变量
}
}
console.log((new ColorPoint('hong1','hong2','hong3').xx))
super到底是什么东西?
我们来看看另一个继承的例子:只能靠代码体会了一时解释很难懂
class Child extends Parent {
constructor(firstName, lastName, age) {
super(firstName, lastName)
this.age = age
}
}其基本等价于:
function Child(firstName, lastName, age) {
Parent.call(this, firstName, lastName)
this.age = age
}
Child.prototype = Object.create(Parent.prototype)
Child.constructor = Child
super的理解
1,super只有在子类继承父类的函数中存在,例如这样的类中必须有super不然就报错
//有extends的类就必须有super(),不然就报错,因为ColorPoint找不到this
class ColorPoint extends Point {
constructor(x, y, color) {
super() //所以要使用super(),这样ColorPoint才能用属于自己的this
}
}
2,super不管作为对象还是函数存在,this永远指向子类它自己,如上面例子:就是this指向的是ColorPoint
3,super()作为函数存在是,只能出现在子类中的constructor函数中,不能出现在原型对象中,并且this是子类它自己。
4,super.xx作为对象存在时,可以出现在构造函数和原型对象中,但只能调用父类的原型对象中的属性或者方法,即super.xx中的xx只能是父类中的原型对象的某一个方法,并且this是子类它自己。
Object.keys(类名.prototype)
//遍历prototype所有属性名和方法,不支持IE8
用ES6的class声明的原型属性和方法,用keys不会遍历出来,ES5则可以
Object.getOwnPropertyNames(类名.prototype)
//不管是不是prototype里面的都遍历出构造函数所有属性名和方法,不支持IE8
